The SI system (Système International d’Unités) is the international system of measurement. A reunited measurement system is essential for scientific research, technological innovation, and global trade.
In Norway, the Norwegian Metrology Service is the national authority responsible for maintaining and managing the SI units. In our laboratories, we ensure that the national references for measurement units are as accurate as possible and traceable to international standards.
The SI consists of seven base units, a large number of derived units, and a collection of prefixes.

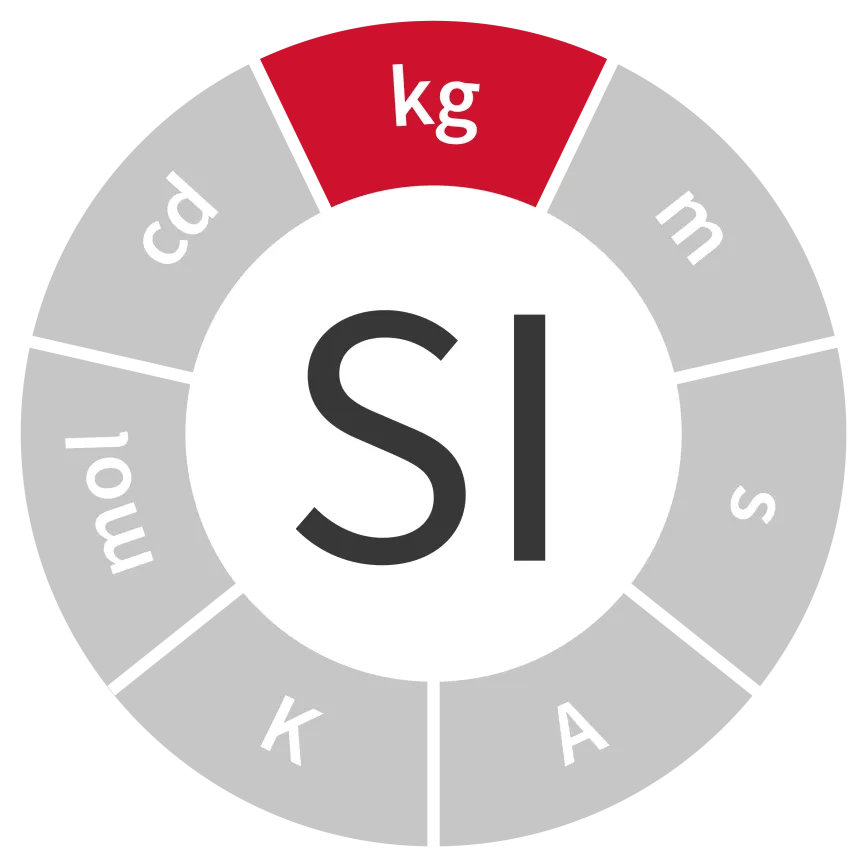
Unit of mass
Symbol: kg
Field: Mass
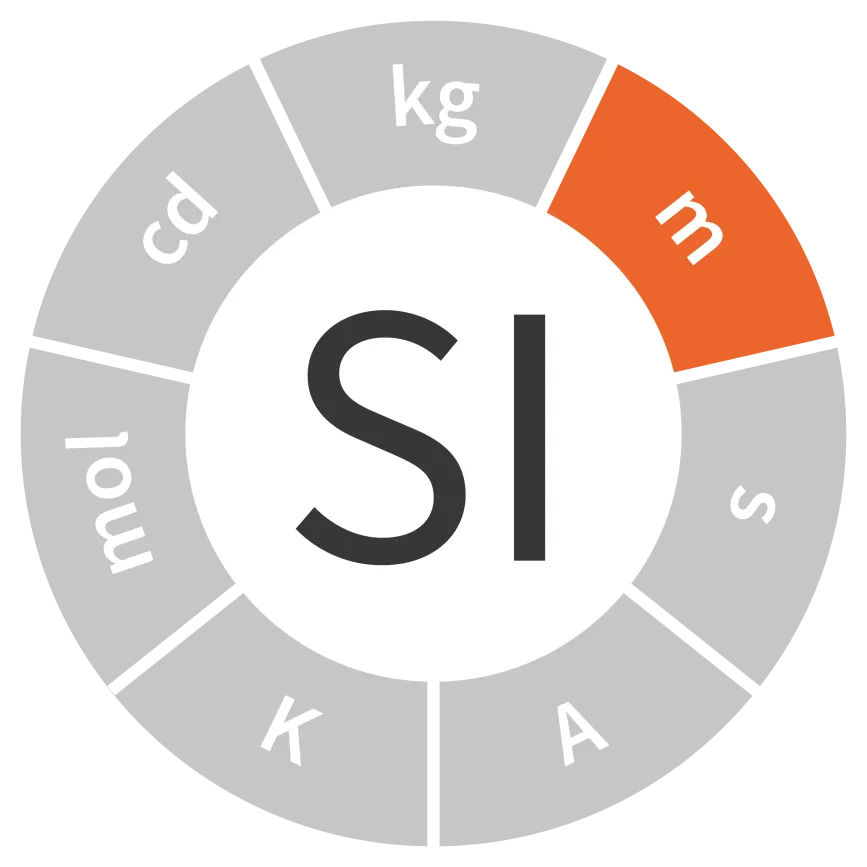
Unit of length
Symbol: m
Field: Length and dimensional measurement
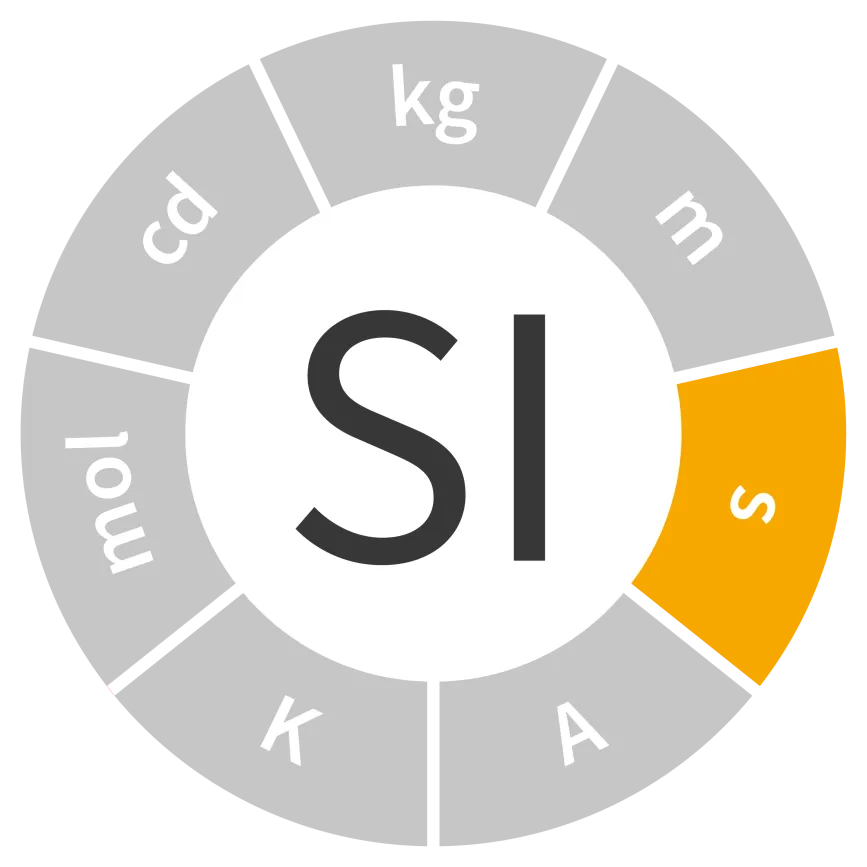
Unit of time
Symbol: s
Field: Time and frequency
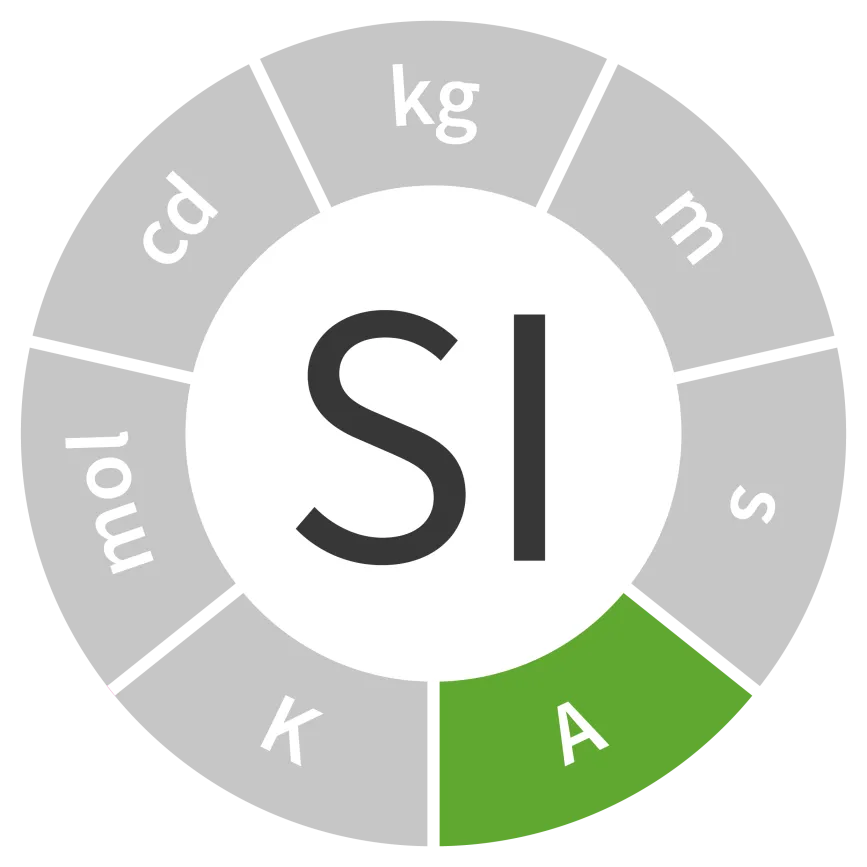
Unit of electric current
Symbol: A
Field: Electrical measurement
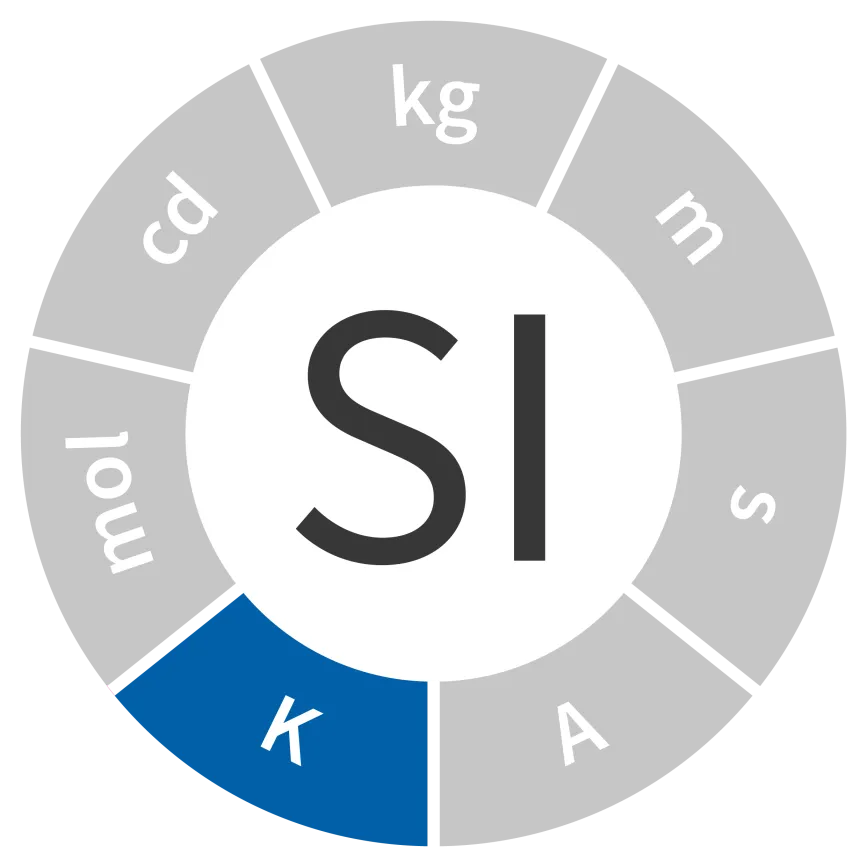
Unit of thermodynamic temperature
Symbol: K
Field: Temperature
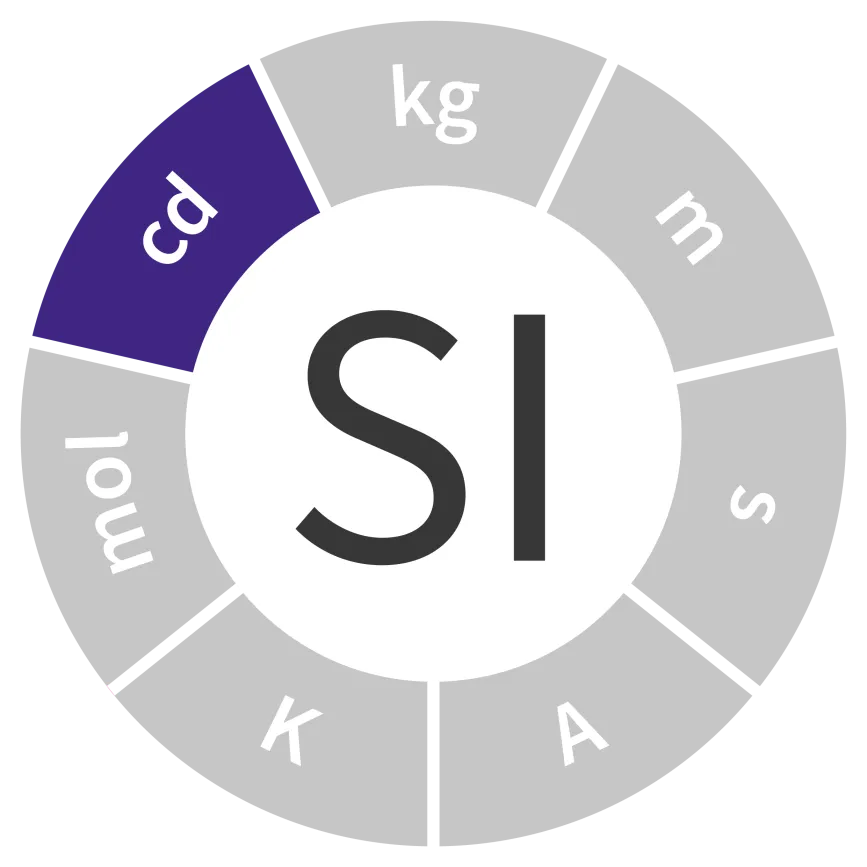
Unit of luminous intensity
Symbol: cd
Field: Optical power
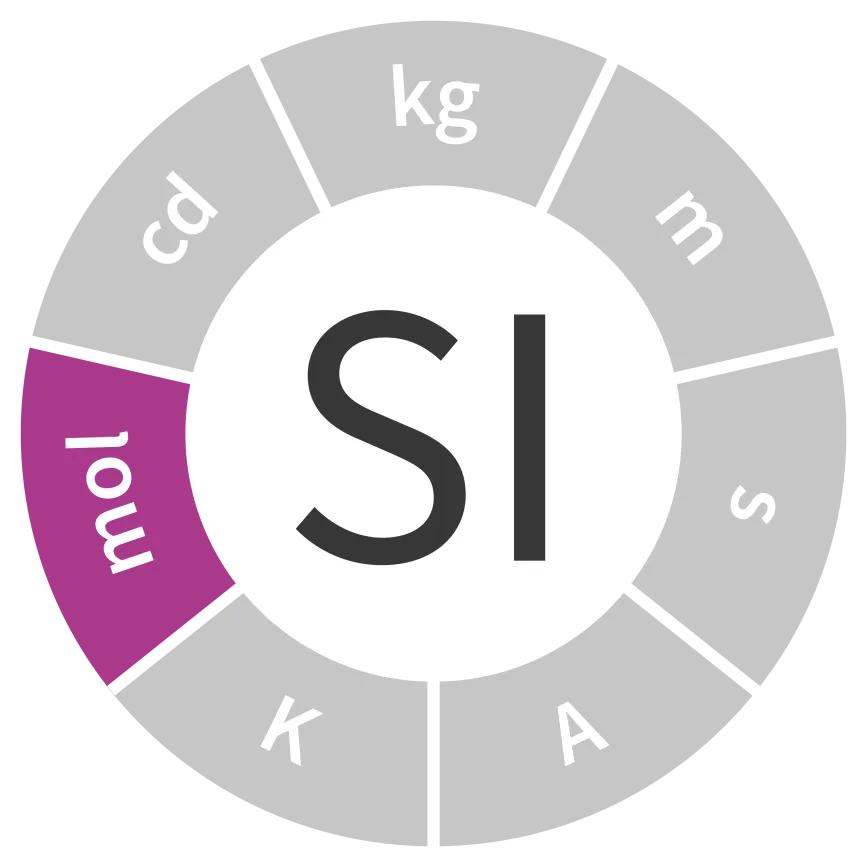
Unit of amount of substance
Symbol: mol
All other measurement units in the SI system are based on these seven fundamental units.
Some derived units have their own names. For example Hertz used to measure frequency (cycles per second), and Newton used to measure force (kilogram times metre divided on square second).
Other units do not have their own names but are expressed through combinations of base units. Examples include:
In this way, we can use the same building blocks to measure many different quantities – from how fast a car travels to how much water a tank holds.